|
Overview
 The term 'fallen arches' is rather a historical one, but is one many people seem to have heard of. What it essentially refers to is a ligament problem in the sole of his foot where these run along its length. In most people these ligaments provide support to the foot when walking and help keep the foot in a normal anatomical position. Some people however seem to have laxity in these ligaments so the foot becomes under undue strain and pain can occur as a result. Causes There are several factors that can contribute to the development of fallen arches. These factors include the following. Genetic abnormality, torn or stretched tendons, amage to the posterior tibial tendon, bone fractures, dislocation of bones, nerve damage, rheumatoid arthritis and other medical conditions. In addition, there are other factors that can increase your risk of developing fallen arches. These risk factors include diabetes, pregnancy, Obesity and Aging. Symptoms Depending on the cause of the flatfoot, a patient may experience one or more of the different symptoms below. Pain along the course of the posterior tibial tendon which lies on the inside of the foot and ankle. This can be associated with swelling on the inside of the ankle. Pain that is worse with activity. High intensity or impact activities, such as running, can be very difficult. Some patients can have difficulty walking or even standing for long periods of time. When the foot collapses, the heel bone may shift position and put pressure on the outside ankle bone (fibula). This can cause pain on the outside of the ankle. Arthritis in the heel also causes this same type of pain. Patients with an old injury or arthritis in the middle of the foot can have painful, bony bumps on the top and inside of the foot. These make shoewear very difficult. Occasionally, the bony spurs are so large that they pinch the nerves which can result in numbness and tingling on the top of the foot and into the toes. Diabetics may only notice swelling or a large bump on the bottom of the foot. Because their sensation is affected, people with diabetes may not have any pain. The large bump can cause skin problems and an ulcer (a sore that does not heal) may develop if proper diabetic shoewear is not used. Diagnosis Your doctor examines your feet to determine two things, whether you have flat feet and the cause or causes. An exam may include the following steps, Checking your health history for evidence of illnesses or injuries that could be linked to flat feet or fallen arches, Looking at the soles of your shoes for unusual wear patterns, Observing the feet and legs as you stand and do simple movements, such as raising up on your toes, Testing the strength of muscles and tendons, including other tendons in the feet and legs, such as the Achilles tendon or the posterior tibial tendon, Taking X-rays or an MRI of your feet. pes valgus Non Surgical Treatment Get shoes made for walking or running. One way to support your arch is to wear good-quality running or walking shoes, says Dr. Gastwirth. "These shoes generally provide good support to the foot." Add support. The top-of-the-line arch support is an orthotic insole, which may cost $900 or more and must be custom-made. "But many people with sore arches will get relief with over-the-counter arch supports for about $10," suggests Judith Smith, M.D., assistant professor of orthopedic surgery at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta. "The thing to remember about arch supports is that your shoe must have enough depth to accommodate them. Otherwise, you'll get a lot of rubbing on the top of your foot, or your heel will come out of the shoe." Most mens shoes are deep enough to accommodate the insoles; women should take their shoes with them to the drugstore when buying the insoles to ensure a good fit. If your heels are high, keep them wide. High heels may be your Achilles' heel--especially if you wear them constantly. "Flatter shoes are no doubt better," says Dr. Sanfilippo. Flat heels help prevent fallen arches and are kinder to your feet if fallen arches have already occurred. "If you must wear high heels, choose styles with a wide heel. Stay away from stiletto heels." Surgical Treatment  Procedures may include the following. Fusing foot or ankle bones together (arthrodesis). Removing bones or bony growths, also called spurs (excision). Cutting or changing the shape of the bone (osteotomy). Cleaning the tendons' protective coverings (synovectomy). Adding tendon from other parts of your body to tendons in your foot to help balance the "pull" of the tendons and form an arch (tendon transfer). Grafting bone to your foot to make the arch rise more naturally (lateral column lengthening). Prevention Donning a first-rate pair of arch supports, therapeutic socks and proper footwear before heading out to enjoy hours of holiday fun is one option to consider. Your podiatrist can help you find just the right ones. Once you have them on, they?ll help ease the amount of pressure being put on your body and keep the blood flowing in the right direction. While you?re standing in line, consider doing a bit of exercise as well. We?re not talking about channeling your inner Jack LaLanne here. Otherwise, you might attract the attention of the mall security guards. Simple ankle rotations and walking in place may help to reduce edema and give your flat feet a bit of a break. If you happen to be in a shopping mall or center where foot massages are available, take advantage of them periodically. They are likely to make you feel better and it?s a great excuse to carve out a few quiet moments for yourself. If you can?t visit a professional, tuck a personal foot massager into your purse. That way, you can lightly massage your own feet during the car ride home. Lastly, there are certain foods and nutritional supplements available that may reduce edema caused by standing on flat feet for hours at a time. The list includes potassium rich foods like raisins, bananas, baby carrots, nuts and yogurt. So, you may want to pack a snack for those trips to the mall or hit the food court before you hit the stores. Overview
People with leg length discrepancy, when one leg is longer than the other, usually have a waddling-type gait where the hips seem to move up and down during walking as the body tries to compensate for the inequality. There are two types of leg length discrepancy. The first type of leg length discrepancy involves a structural defect, where one bone is longer or shorter than the corresponding bone of the other limb. This can occur within the femur (upper leg bone) or the tibia and fibular (lower leg bones). Functional leg length discrepancy results from altered mechanics due to a malalignment in the spine or lower extremity.  Causes There are many causes of leg length discrepancy. Some include, A broken leg bone may lead to a leg length discrepancy if it heals in a shortened position. This is more likely if the bone was broken in many pieces. It also is more likely if skin and muscle tissue around the bone were severely injured and exposed, as in an open fracture. Broken bones in children sometimes grow faster for several years after healing, causing the injured bone to become longer. A break in a child's bone through the growth center near the end of the bone may cause slower growth, resulting in a shorter leg. Bone infections that occur in children while they are growing may cause a significant leg length discrepancy. This is especially true if the infection happens in infancy. Inflammation of joints during growth may cause unequal leg length. One example is juvenile arthritis. Bone diseases may cause leg length discrepancy, as well. Examples are, Neurofibromatosis, Multiple hereditary exostoses, Ollier disease. Other causes include inflammation (arthritis) and neurologic conditions. Sometimes the cause of leg length discrepancy is unknown, particularly in cases involving underdevelopment of the inner or outer side of the leg, or partial overgrowth of one side of the body. These conditions are usually present at birth, but the leg length difference may be too small to be detected. As the child grows, the leg length discrepancy increases and becomes more noticeable. In underdevelopment, one of the two bones between the knee and the ankle is abnormally short. There also may be related foot or knee problems. Hemihypertrophy (one side too big) or hemiatrophy (one side too small) are rare leg length discrepancy conditions. In these conditions, the arm and leg on one side of the body are either longer or shorter than the arm and leg on the other side of the body. There may also be a difference between the two sides of the face. Sometimes no cause can be found. This is known as an "idiopathic" difference. Symptoms LLD do not have any pain or discomfort directly associated with the difference of one leg over the other leg. However, LLD will place stress on joints throughout the skeletal structure of the body and create discomfort as a byproduct of the LLD. Just as it is normal for your feet to vary slightly in size, a mild difference in leg length is normal, too. A more pronounced LLD, however, can create abnormalities when walking or running and adversely affect healthy balance and posture. Symptoms include a slight limp. Walking can even become stressful, requiring more effort and energy. Sometimes knee pain, hip pain and lower back pain develop. Foot mechanics are also affected causing a variety of complications in the foot, not the least, over pronating, metatarsalgia, bunions, hammer toes, instep pain, posterior tibial tendonitis, and many more. Diagnosis A qualified musculoskeletal expert will first take a medical history and conduct a physical exam. Other tests may include X-rays, MRI, or CT scan to diagnose the root cause. Non Surgical Treatment The way in which we would treat a LLD would depend on whether we have an anatomical or functional difference. To determine which one is causing the LLD you will need to get your legs measured. This is the easiest way to determine if it is anatomical or functional. With a functional LLD we must first determine the cause and treat the cause. Should the cause be one that is not correctable then we may need to treat the LLD as if it were an anatomical or may have to treat the opposite leg to improve one's gait. As for the anatomical LLD, we may start off with a heel lift only in the shoe and follow up to see if we will need to put the lift full sole on the bottom of the shoe. This is determined by the affects that a heel lift in one shoe may have on that knee. Should the LLD be more than 1/4 inch we usually recommend starting between 1/8 inch to 1/4 inch less than the actual amount and let the body adjust to the change and then raise up to the measured amount later.  functional leg length discrepancy treatment Surgical Treatment Surgeries for LLD are designed to do one of three general things ? shorten the long leg, stop or slow the growth of the longer or more rapidly growing leg, or lengthen the short leg. Stopping the growth of the longer leg is the most commonly utilized of the three approaches and involves an operation known as an epiphysiodesis , in which the growth plate of either the lower femur or upper tibia is visualized in the operating room using fluoroscopy (a type of real-time radiographic imaging) and ablated , which involves drilling into the region several times, such that the tissue is no longer capable of bone growth. Because the epiphyseal growth capabilities cannot be restored following the surgery, proper timing is crucial. Usually the operation is planned for the last 2 to 3 years of growth and has excellent results, with children leaving the hospital within a few days with good mobility. However, it is only appropriate for LLD of under 5cm. Overview
 Heel pain is a problem for many people. It makes standing and even walking around for long periods of time very uncomfortable. Several different conditions can lead to uncomfortable heels, but the most common culprit is plantar fasciitis. This is the inflammation and swelling of the plantar fascia, a tendon that runs along the sole of your foot and attaches to the bottom of the calcaneus, or heel bone. Repeated hard impacts or strain from overuse causes micro-tears to develop in the tendon, irritating it. The minor damage compounds over time and causes the tissue to swell and tighten, painfully pulling on the heel bone. Causes The most common cause of heel pain in adults is plantar fasciitis, which is an inflammation of the band of tissue in the sole that connects the heel to the toes and forms the natural foot arch. Plantar fasciitis may or may not be complicated by a calcaneal spur, a small bone growth that protrudes out of the heel. Plantar fasciitis may also be referred to as plantar fasciosis. In contrast to fasciitis, which essentially means inflammation, fasciosis refers to degeneration of the tissue. In fact, if left untreated, acute plantar fasciitis may develop into a chronic painful condition, which results in slow and irreversible degeneration of the fascia, hence plantar fasciosis. The location of the pain is usually exactly under the heel but may also occur in the arch of the foot. Pain typical to plantar fasciitis is that which feels worse when arising on to your feet such as in mornings or after sitting down for a while, and usually progresses in severity when left untreated. Symptoms Symptoms may also include swelling that is quite tender to the touch. Standing, walking and constrictive shoe wear typically aggravate symptoms. Many patients with this problem are middle-aged and may be slightly overweight. Another group of patients who suffer from this condition are young, active runners. Diagnosis Depending on the condition, the cause of heel pain is diagnosed using a number of tests, including medical history, physical examination, including examination of joints and muscles of the foot and leg, X-rays. Non Surgical Treatment Treatment of plantar fasciitis begins with first-line strategies, which you can begin at home. Stretching exercises. Exercises that stretch out the calf muscles help ease pain and assist with recovery. Avoid going barefoot. When you walk without shoes, you put undue strain and stress on your plantar fascia. Ice. Putting an ice pack on your heel for 20 minutes several times a day helps reduce inflammation. Place a thin towel between the ice and your heel; do not apply ice directly to the skin. Limit activities. Cut down on extended physical activities to give your heel a rest. Shoe modifications. Wearing supportive shoes that have good arch support and a slightly raised heel reduces stress on the plantar fascia. Medications. Oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation. Surgical Treatment If treatment hasn't worked and you still have painful symptoms after a year, your GP may refer you to either an orthopaedic surgeon, a surgeon who specialises in surgery that involves bones, muscles and joints or a podiatric surgeon, a podiatrist who specialises in foot surgery. Surgery is sometimes recommended for professional athletes and other sportspeople whose heel pain is adversely affecting their career. Plantar release surgery is the most widely used type of surgery for heel pain. The surgeon will cut the fascia to release it from your heel bone and reduce the tension in your plantar fascia. This should reduce any inflammation and relieve your painful symptoms. Surgery can be performed either as open surgery, where the section of the plantar fascia is released by making a cut into your heel or endoscopic or minimal incision surgery - where a smaller incision is made and special instruments are inserted through the incision to gain access to the plantar fascia. Endoscopic or minimal incision surgery has a quicker recovery time, so you will be able to walk normally much sooner (almost immediately), compared with two to three weeks for open surgery. A disadvantage of endoscopic surgery is that it requires both a specially trained surgical team and specialised equipment, so you may have to wait longer for treatment than if you were to choose open surgery. Endoscopic surgery also carries a higher risk of damaging nearby nerves, which could result in symptoms such as numbness, tingling or some loss of movement in your foot. As with all surgery, plantar release carries the risk of causing complications such as infection, nerve damage and a worsening of your symptoms after surgery (although this is rare). You should discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both techniques with your surgical team. heel cushions Prevention  Before you get out of bed in the morning, and then periodically throughout the day, do the following exercises to increase flexibility and ease pain. Slowly flex your foot and toes to stretch the tissue on the bottom of your sore foot. Hold the stretch for 10 counts. Relax and repeat. Do gentle ankle rolls to keep the tissues around the ankle and on the back of the heel flexible. Sit on the edge of your bed and roll your foot back and forth over a tennis ball. Overview
 Morton's neuroma is an inflammation of the nerves in the foot that go to the toes. Although the name includes the word ?neuroma,? it is not really a tumor. It can affect any of the toes in the foot. However, it most often affects the nerves that run between the third and fourth, or second and third toes. Morton's neuroma is an inflammation of the nerves in the foot that go to the toes. Although the name includes the word ?neuroma,? it is not really a tumor. It can affect any of the toes in the foot. However, it most often affects the nerves that run between the third and fourth, or second and third toes.Causes Although in many areas of medicine, it?s easy to pinpoint the exact source of a problem (the way a specific germ causes a certain illness with recognizable symptoms), neuromas are harder to categorize. While there isn?t really one exact cause, podiatric physicians tend to agree that a neuroma can occur in response to the irritation of a nerve by one or more factors. Abnormality in foot function or foot mechanics: In other words, a foot that doesn?t move the way science thinks it should. In general, this means a pronated foot (one with an excessive rolling motion when the patient is walking, running or doing any kind of activity), because it causes excessive strain on the nerve. If you are not certain whether or not this is a problem for you, ask your podiatric physician, who will be able to examine your feet, as well as the wear pattern on your shoe, and give you an answer. Foot mechanics, and problems with them, tend to run in families, so if you know that a relative has had foot pain similar to yours, be sure to mention it. Symptoms You may initially experience a tingling sensation in the space between your toes, which gets worse over time. This leads to cramp in your toes and a sharp shooting or burning pain on the ball of your foot or at the base of your toes. The pain is often worse when walking or wearing shoes that press on the affected area. This is caused by irritation of the nerve between your toe bones (metatarsal bones). The tingling will eventually lead to pain, which can get worse over time. You may also experience cramping of your toes. The pain is usually felt as a sharp shooting or burning pain on the ball of the foot or at the base of the toes, which is often made worse when you're walking. Some people with Morton's neuroma feel anxious about walking or even placing their foot on the ground. The pain is likely to be more intense if you wear tight shoes, so wearing shoes that have more room in the toe area can help. Rubbing your foot may also lessen the pain. Diagnosis A GP (general practitioner, primary care physician) or a podiatrist (foot specialist doctor) will ask the patient to describe the pain as well as its intensity, when symptoms started, what types of shoes are worn, as well as some questions about their job, lifestyle and hobbies. The doctor will then examine the foot and try to locate the affected nerve. This may involve attempting to reproduce symptoms by manipulating the foot. In order to get a detailed image of the inside of the food, one of the following scans may be ordered. X-ray, this is a type of high-energy radiation. In low doses they are used to diagnose diseases and condition by making pictures of the inside of the body. In higher doses they are used to treat cancer. This procedure is non-invasive and painless. Ultrasound scan, high frequency sound waves are pointed at a specific part of the body, which in this case is the foot. The ultrasound waves bounce of tissues; their echoes are then converted into a picture, called a sonogram. This allows the doctor to get an inside view of the foot. This procedure is non-invasive and painless. MRI (magnetic resonance imagining) a device that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the body. Unlike CT scanning or general x-ray studies, no ionizing radiation is involved with an MRI. This procedure is non-invasive and painless. The doctor will have to rule out other conditions which may have similar symptoms, including capsulitis, bursitis, or Freiberg's disease. Non Surgical Treatment Treatment strategies for Morton's neuroma range from conservative to surgical management. The conservative approach to treating Morton's neuroma may benefit from the involvement of a physical therapist. The physical therapist can assist the physician in decisions regarding the modification of footwear, which is the first treatment step. Recommend soft-soled shoes with a wide toe box and low heel (eg, an athletic shoe). High-heeled, narrow, nonpadded shoes should not be worn, because they aggravate the condition. The next step in conservative management is to alter alignment of the metatarsal heads. One recommended action is to elevate the metatarsal head medial and adjacent to the neuroma, thereby preventing compression and irritation of the digital nerve. A plantar pad is used most often for elevation. Have the patient insert a felt or gel pad into the shoe to achieve the desired elevation of the above metatarsal head. Other possible physical therapy treatment ideas for patients with Morton's neuroma include cryotherapy, ultrasonography, deep tissue massage, and stretching exercises. Ice is beneficial to decrease the associated inflammation. Phonophoresis also can be used, rather than just ultrasonography, to further decrease pain and inflammation.  Surgical Treatment Surgery for Morton's neuroma is usually a treatment of last resort. It may be recommended if you have severe pain in your foot or if non-surgical treatments haven't worked. Surgery is usually carried out under local anaesthetic, on an outpatient basis, which means you won't need to stay in hospital overnight. The operation can take up to 30 minutes. The surgeon will make a small incision, either on the top of your foot or on the sole. They may try to increase the space around the nerve (nerve decompression) by removing some of the surrounding tissue, or they may remove the nerve completely (nerve resection). If the nerve is removed, the area between your toes may be permanently numb. After the procedure you'll need to wear a special protective shoe until the affected area has healed sufficiently to wear normal footwear. It can take up to four weeks to make a full recovery. Most people (about 75%) who have surgery to treat Morton's neuroma have positive results and their painful symptoms are relieved. There are not one but two different types of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital indicates you are born with it. One leg is structurally shorter than the other. As a result of developmental phases of aging, the brain senses the step pattern and identifies some variance. The body usually adapts by dipping one shoulder over to the "short" side. A difference of under a quarter inch isn't grossly abnormal, does not need Shoe Lifts to compensate and usually won't have a serious effect over a lifetime.
 Leg length inequality goes typically undiscovered on a daily basis, however this issue is easily remedied, and can eliminate quite a few cases of back discomfort. Therapy for leg length inequality usually involves Shoe Lifts. They are affordable, normally costing under twenty dollars, compared to a custom orthotic of $200 or even more. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe. Back pain is the most widespread health problem afflicting men and women today. Over 80 million people suffer from back pain at some point in their life. It is a problem which costs companies millions yearly due to time lost and production. Fresh and more effective treatment methods are continually sought after in the hope of decreasing the economic impact this condition causes.  Men and women from all corners of the earth suffer the pain of foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In a lot of these cases Shoe Lifts are usually of worthwhile. The lifts are capable of alleviating any discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by numerous specialist orthopaedic orthopedists. So that they can support the body in a well-balanced fashion, the feet have got a vital part to play. Despite that, it's often the most neglected region of the body. Many people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force exerted on the feet. This will cause other body parts such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts ensure that appropriate posture and balance are restored.  Overview OverviewHammer toes can occur when feet are crammed into shoes so tight that the front of the toes are pushed against the front of the shoes for prolonged periods of time. One or more toes then remain bent with the middle knuckle pointing up, even when shoes are taken off. If the condition is left untreated and tight footwear is continually worn, these bent toes can become so rigid that they can no longer straighten out on their own. While any shoes that are too tight can lead to this condition, high heels seem to be a big culprit since the elevated ankle causes more weight to push the toes forward. This may explain why the condition affects more women than men. Causes This condition is greatly influenced by the footwear we choose. Ladies who wear high heels are a perfect example. High heels force the toes to overlap and bend at the middle joint of the toe, resulting in hammertoe. But high heels are not the only culprits. Anyone who wears shoes that are too tight is increasing their risk of developing hammertoe. This progressive condition, which will only get better with treatment, can cause pain as the toes are forced to bend unnaturally.  Symptoms SymptomsA hammer toe may be painful, especially when irritated by a shoe. All four toe conditions may cause cramps in the toes, foot and leg due to the abnormal function of the tendons in the foot. If a mallet toe has occurred, you are likely to suffer from a corn at the end of the toe. A hammertoe may cause a corn on the top of the toe. Infections and ulcers can also occur. In severe cases a mallet toe, trigger toe, claw toe or a hammer toe may create a downward pressure on the foot, which can result in hard skin and corns on the soles of the feet. Diagnosis The treatment options vary with the type and severity of each hammer toe, although identifying the deformity early in its development is important to avoid surgery. Your podiatric physician will examine and X-ray the affected area and recommend a treatment plan specific to your condition. Non Surgical Treatment Hammertoes that are not painful (asymptomatic) and still flexible may not require treatment. In mild cases, open-toed, low-heeled, or wider shoes and foam or moleskin pads can provide symptomatic relief by reducing pressure. Taping (strapping) the affected toe can help to reduce deformity and pain. Physical therapy to instruct patients in exercises that passively stretch tight structures and strengthen weak foot intrinsic muscles is also hammertoe helpful with mild cases. Periodic trimming (debridement) of corns (clavi, helomata) by a podiatrist can provide temporary relief. Corticosteroid injections are often very effective in reducing pain. Surgical Treatment Surgery is the approach that is often necessary to correct hammertoe that fails to respond to nonsurgical management. Surgery is appropriate when the muscles and tendons involved in a hammertoe problem have become so tight that the joints are rigid, misaligned and unmovable. There are a number of surgical techniques for dealing with the complex range of joint, bone, muscle, tendon and ligament abnormalities that define each hammertoe's make-up. To correct a hammertoe deformity, the surgeon's goal is to restore the normal alignment of the toe joint, relieving the pressure that led to the hammertoe's development (this should also relieve the pain, as well). To do this, he or she may remove part of the boney structure that creates a prominence at the top of the joint. Tighten or loosen the muscles, tendons and ligaments around the toe joints. Realign the toe bones by cutting one or more and shifting their position, realigning muscles, tendons and ligaments accordingly. Use screws, wires or plates to hold the joint surfaces together until they heal. Reconstruct a badly damaged joint or replace it with an artificial implant.  Overview OverviewA Hammer toes is a toe that is contracted at the PIP joint (middle joint in the toe), potentially leading to severe pressure and pain. Ligaments and tendons that have tightened cause the toe's joints to curl downwards. Hammer toes may occur in any toe except the big toe. There is often discomfort at the top part of the toe due to rubbing against the shoe. Causes Many disorders can affect the joints in the toes, causing pain and preventing the foot from functioning as it should. A mallet toe occurs when the joint at the end of the toe cannot straighten. Excessive rubbing of the mallet toe against the top of the shoe can lead to pain and the development of a corn. The tip of the toe is often turned down against the shoe causing pressure and discomfort. Arthritis can also lead to many forefoot deformities including mallet toes. Mallet toes can cause extreme discomfort, and can be aggravated if restrictive or improperly fitting footwear is worn for a prolonged period of time.  Symptoms A toe stuck in an upside-down "V" is probably a hammertoe. Some symptoms are, pain at the top of the bent toe when putting on a shoe. Corns forming on the top of the toe joint. The toe joint swelling and taking on an angry red colour. Difficulty in moving the toe joint and pain when you try to so. Pain on the ball of the foot under the bent toe. Seek medical advice if your feet regularly hurt, you should see a doctor or podiatrist. If you have a hammertoe, you probably need medical attention. Ask your doctor for a referral to a podiatrist or foot surgeon. Act now, before the problem gets worse. Diagnosis First push up on the bottom of the metatarsal head associated with the affected toe and see if the toe straightens out. If it does, then an orthotic could correct the problem, usually with a metatarsal pad. If the toe does not straighten out when the metatarsal head is pushed up, then that indicates that contracture in the capsule and ligaments (capsule contracts because the joint was in the wrong position for too long) of the MTP joint has set in and surgery is required. Orthotics are generally required post-surgically. Non Surgical Treatment If your hammertoe problem is diagnosed as flexible hammertoe, there are a number of nonsurgical treatments that may be able to straighten out your toe or toes and return them to their proper alignment. Padding and Taping. Your physician may pad the boney top-part of your hammertoe as a means of relieving pain, and may tape your toes as a way to change their position, correct the muscle imbalance and relieve the pressure that led to the hammertoe's development. Medication. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin and ibuprofen can help deal with inflammation, swelling and pain caused by your hammertoe. Cortisone injections may be prescribed for the same purpose. If your hammertoe is a consequence of arthritis, your physician may prescribe medications for that. Surgical Treatment If these non-invasive treatments don?t work, or if the joint is rigid, a doctor?s only recourse may be to perform surgery. During the surgery, the doctor makes an incision and cuts the tendon to release it or moves the tendon away from or around the joint. Sometimes part of the joint needs to be removed or the joint needs to be fused. Each surgery is different in terms of what is needed to treat the hammertoe. Normally after any foot surgery, patients use a surgical shoe for four to six weeks, but often the recovery from hammertoe surgery is more rapid than that. An unfortunate reality is that hammertoe can actually return even after surgery if a patient continues to make choices that will aggravate the situation. Though doctors usually explain pretty clearly what needs to be done to avoid this.  Prevention Good circulation is essential. When you're sitting down, put your feet up. If you've been sitting for a while, stretch your legs and feet. Give yourself a foot massage or trade foot massages with someone you love. A warm foot bath is also a good idea. Most people have one foot that's bigger than the other. Fit your shoes to the bigger foot. Buy shoes at the end of the day, as feet tend to swell a bit and you will get a better sense of fit. When buying shoes, wear the socks that you will be using when wearing that shoe. For example, wear an athletic sock when buying athletic shoes and a dress sock when purchasing dress shoes. If the shoe does not feel good at the time of purchase, then it will never feel good.
Overview
 A bunion is enlargement of bone or tissue that develops at the joint that connects your big toe to your foot. The bones, muscles, ligaments and tendons of your feet normally are well-balanced to distribute your body's weight while standing, walking and running. When the joint, called the metatarsophalangeal joint, or MTP joint, experiences abnormal, prolonged stress in terms of weight distribution or squeezing of the toes within the shoe, the result can be the deformity called a bunion. Generally, a bunion develops when, as a response to prolonged stress, your big toe begins bending toward your foot's smaller toes and puts pressure on your MTP joint, forcing it to bulge outward (the term "bunion" comes from the Latin word for "enlargement"). There is no "standard" bunion, however, but rather a complex range of joint, bone and tendon abnormalities that can cause variation in each bunion's make-up. A bunion is enlargement of bone or tissue that develops at the joint that connects your big toe to your foot. The bones, muscles, ligaments and tendons of your feet normally are well-balanced to distribute your body's weight while standing, walking and running. When the joint, called the metatarsophalangeal joint, or MTP joint, experiences abnormal, prolonged stress in terms of weight distribution or squeezing of the toes within the shoe, the result can be the deformity called a bunion. Generally, a bunion develops when, as a response to prolonged stress, your big toe begins bending toward your foot's smaller toes and puts pressure on your MTP joint, forcing it to bulge outward (the term "bunion" comes from the Latin word for "enlargement"). There is no "standard" bunion, however, but rather a complex range of joint, bone and tendon abnormalities that can cause variation in each bunion's make-up.Causes Bunions most commonly affect women. Some studies report that bunion symptoms occur nearly 10 times more frequently in women. It has been suggested that tight-fitting shoes, especially high-heel and narrow-toed shoes, might increase the risk for bunion formation. Tight footwear certainly is a factor in precipitating the pain and swelling of bunions. Complaints of bunions are reported to be more prevalent in people who wear shoes than in barefoot people. Other risk factors for the development of bunions include abnormal formation of the bones of the foot at birth (congenital) and arthritic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. In some cases, repetitive stresses to the foot can lead to bunion formation. Bunions are common in ballet dancers. Symptoms The dominant symptom of a bunion is a big bulging bump on the inside of the base of the big toe. Other symptoms include swelling, soreness and redness around the big toe joint, a tough callus at the bottom of the big toe and persistent or intermittent pain. Diagnosis Generally, observation is adequate to diagnose a bunion, as the bump is obvious on the side of the foot or base of the big toe. However, your physician may order X-rays that will show the extent of the deformity of the foot. Non Surgical Treatment Bunions can develop at any time. Although bunions often require no medical treatment you should consult your family doctor/chiropodist/podiatrist. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of your bunion and the amount of pain it causes you. Although they don't always cause problems, bunions are permanent unless surgically corrected. If the cushioning sac of fluid (bursa) over the affected joint becomes inflamed (bursitis), a bunion can be very painful and interfere with your normal activities. Bunions may get larger and more painful, making nonsurgical treatment less effective. Apply a non-medicated bunion pad around the bony bump. If a bunion becomes inflamed or painful, apply an ice pack two to three times daily to help reduce swelling. Wear shoes with a wide and deep toe box. Avoid shoes with heels higher than 2 inches (5.1 centimeters). 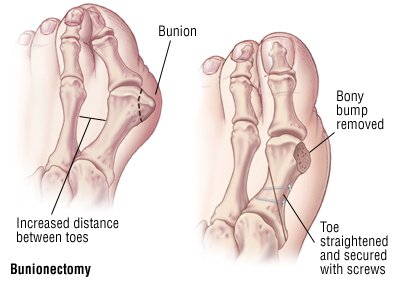 Surgical Treatment The most significant portion of the bunion surgery is re-aligning the bones. This is performed though bone cuts or a fusion involving the first metatarsal. The severity of the bunion determines where the bone will be cut or fused. Mild or moderate bunions can be corrected close to the big toe joint. Moderate or large bunions often require that the bone work be performed further away from the big toe joint to swing the bone in the proper position. |
|
